SICU or MICU? A Guide to Intensive Care Unit Options
The SICU specializes in post-surgical recovery and trauma care, while the MICU manages severe, non-surgical medical conditions. Both units demand critical thinking, quick decision-making, and physical and emotional resilience, with opportunities for specialization like CCRN in the SICU or NP in the MICU.
Choosing a career in the SICU or MICU can be a fulfilling path for those interested in providing critical care to patients in life-threatening conditions. Both units offer unique opportunities, but they cater to different patient needs and require distinct skill sets.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
YOUR PATH TO SUCCESS BEGINS HERE
Understanding the key differences in SICU vs MICU patient care, work environment, and career growth can help you decide which unit aligns best with your interests and long-term professional goals. Continue reading to find out!
What Is the SICU (Surgical Intensive Care Unit)?
The Surgical Intensive Care Unit (SICU) is a specialized hospital area that provides intense, round-the-clock care for patients who have had major surgeries or experienced severe trauma. Its primary purpose is to monitor and support patients during the critical period right after surgery when they’re at the highest risk for complications.
Patients who have been in serious car accidents and need immediate care for injuries to multiple organs go to the SICU. Here, the medical team is prepared to handle complex situations and prevent complications, making sure patients have the best chance to heal properly.
What Is the MICU (Medical Intensive Care Unit)?
The Medical Intensive Care Unit (MICU) is a hospital unit dedicated to providing intensive care for patients with serious medical conditions that need close, constant monitoring and treatment. Unlike the SICU, which focuses on surgical patients, the MICU is for those who have critical illnesses or severe complications from medical conditions.
Doctors and nurses in the MICU use advanced tools and treatments to stabilize these patients, watch for changes, and provide life-saving support. The goal is to help patients recover by carefully managing complex conditions in a controlled environment.
Key Differences between the SICU and the MICU
Though the distinction between SICU and MICU has now been explained, a deeper dive into the specifics will enhance your understanding. So let’s look at the patient types, team structure, and procedures employed in each.
Patient types and conditions treated
Patients admitted to the SICU typically experience the following:
- Cardiac Surgery: Patients recovering from heart bypass surgery.
- Organ Transplants: Liver, kidney, or heart transplant patients needing constant monitoring.
- Trauma from Accidents: Severe injuries from car accidents or falls.
- Major Abdominal Surgeries: Complicated bowel surgeries or removal of large tumors.
- Neurosurgery: Recovery from brain surgery or spine procedures.
Whereas, cases taken to MICU include:
- Severe Infections: Patients with sepsis requiring intensive antibiotics and support.
- Respiratory Failure: Conditions like pneumonia or COPD needing ventilator support.
- Acute Heart Failure: Sudden worsening of heart disease that needs close monitoring.
- Stroke: Severe cases where brain swelling or bleeding is present.
- Multi-Organ Failure: Patients with multiple organs, like kidneys and liver, failing at once.
Care team structure
In both the SICU and MICU, the core care team includes highly trained specialists, but they focus on different areas of care.
The SICU team primarily includes surgical specialists, such as surgeons, anesthesiologists, and respiratory therapists, who work together to support patients after major surgeries or trauma. Their goal is to manage postoperative care and help patients recover from surgical complications.
The MICU team, on the other hand, consists of medical specialists like intensivists, pulmonologists, and cardiologists. They focus on stabilizing patients with severe, life-threatening medical conditions, such as organ failure, infections, or respiratory crises.
Common procedures and equipment

Common procedures used in surgical care include:
- Post-operative care: Managing vital signs, pain, and medication after surgery.
- Wound management: Cleaning and dressing surgical wounds to prevent infection.
- Sedation management: Adjusting sedatives to keep patients calm and comfortable.
The team at SICU makes use of ventilators (to assist patients with breathing), surgical drains (to remove fluids from wounds), and ECG machines (for monitoring heart rhythms to detect irregularities).
On the contrary, procedures employed in MICU include:
- Intubation: Inserting a breathing tube for patients with respiratory failure.
- Hemodynamic monitoring: Tracking blood flow and blood pressure.
- Dialysis: The process that removes waste, toxins, and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys are no longer able to function properly.
The healthcare professionals at MICU typically use equipment like ventilators, dialysis machines, and CVCs (Central Venous Catheters) to help patients.
Recovery time and duration
Patients in the SICU are generally recovering from major surgeries or traumatic events, so their stay is short but highly intensive. They often remain in the SICU for just a few days, depending on the complexity of their surgery or the extent of their trauma.
During this time, they receive constant monitoring and support to ensure a stable recovery from immediate post-surgical or trauma-related risks.
In contrast, patients in the MICU typically face longer recovery periods as they battle severe medical conditions that require ongoing, specialized treatment. MICU stays can vary significantly, lasting from several days to weeks, depending on the seriousness of the underlying condition.
Recovery in the MICU can be slower and may include managing complications from chronic diseases or acute crises, like respiratory rehabilitation or infection recovery, to gradually stabilize the patient’s health.
Career Opportunities in the SICU and the MICU
Careers in the SICU or MICU offer roles like doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists, with responsibilities focused on critical patient care.
Job roles in the SICU
In the SICU, several key roles work together to support patients recovering from major surgeries or trauma. Here’s a quick look at each role:
- Registered Nurses (RNs): RNs in the SICU provide constant patient monitoring, administer medications, manage pain, and respond quickly to any complications. They play a central role in patient care and communicate updates to families.
- Surgical Technologists: These professionals help set up the SICU and assist during surgeries, ensuring that equipment and supplies are sterile and ready. They support both surgical teams and SICU staff to maintain a safe environment for patients.
- Anesthesiologists: Anesthesiologists manage patients’ pain and sedation levels, ensuring comfort and safety during and after surgeries. They oversee anesthesia needs, particularly in cases of emergency post-surgical care.
- Respiratory Therapists: In the SICU, respiratory therapists assist patients who have difficulty breathing, often managing ventilators and other respiratory equipment. They work to improve lung function and monitor oxygen levels.
In the SICU, each role is essential to providing comprehensive, continuous care that helps patients recover safely from complex surgeries and trauma.
Job roles in the MICU
A wide range of roles await those interested in working in the MICU to manage patients with severe medical conditions. Here are some of the key roles:
- Intensivists (Critical Care Physicians): Intensivists oversee the care of critically ill patients, managing complex medical conditions and coordinating the treatment plan to stabilize and monitor patients’ health.
- Pulmonologists: These doctors specialize in lung conditions and help manage respiratory issues such as respiratory failure or severe pneumonia, often overseeing ventilator support and lung treatments.
- Cardiologists: Cardiologists focus on heart-related issues, managing patients with acute heart failure, arrhythmias, or other severe heart conditions.
- Nephrologists: These specialists manage kidney-related problems, often overseeing dialysis treatments for patients with kidney failure or those at risk of kidney injury.
Each of these roles is crucial in delivering specialized care to patients with life-threatening medical conditions.
Salary expectations and specialization opportunities
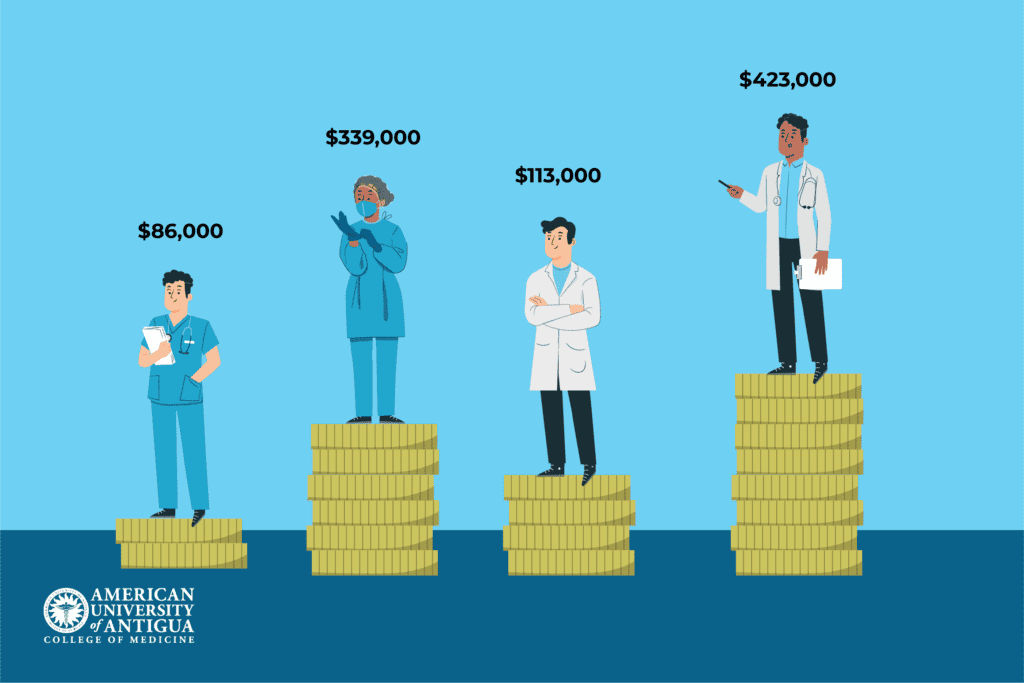
Healthcare professionals in the SICU typically earn between $86,000 (registered nurses) and $339,000 (anesthesiologists) annually, with salaries varying by role and experience. Higher pay and more senior positions may result from specialization in fields like critical care nursing or becoming an advanced practice registered nurse.
In the MICU, salaries are generally higher, ranging from $113,000 (pulmonologists) to $423,000 (cardiologists), depending on experience and specialization. Some other roles in MICU, like nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs), earn a relatively lower annual income.
All things considered, specializing in either unit can open doors to leadership positions and increase income potential.
Which ICU Is Right for Your Career Path?
Choosing between a career in the SICU or MICU depends on your personal interests, strengths, and long-term career goals. Both units offer rewarding, dynamic opportunities, but each has its own focus.
The SICU is ideal for those who enjoy hands-on care for patients recovering from surgeries or trauma, requiring skills in critical thinking, quick decision-making, and wound management.
The MICU, on the other hand, is better suited for individuals interested in managing complex, severe medical conditions like respiratory failure or organ failure. Success in the MICU requires strong problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and expertise in managing chronic diseases.
Whether you’re drawn to surgical recovery or intensive medical care, your decision should align with your passion for patient care, preferred work environment, and desire for specialization.
Conclusion
Both the SICU and MICU offer rewarding career paths, but they cater to different interests and strengths. The SICU focuses on post-surgical recovery and trauma care, requiring quick decision-making and surgical expertise. The MICU, on the other hand, involves managing severe medical conditions, demanding strong problem-solving skills and specialized knowledge.
With the differences in mind, both units provide opportunities for further specialization, allowing professionals to advance their careers based on their interests and strengths. Before deciding on your future path, take some time to reflect on your preferences and strengths to land a role that fulfills you and lets you thrive!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the typical work schedule for SICU and MICU nurses?
SICU and MICU nurses often work 12-hour shifts, including nights, weekends, and holidays, due to the critical nature of care in both units.
What are the physical and emotional challenges of working in the SICU and MICU?
Professionals working in these units face physically demanding tasks like lifting patients and monitoring equipment, while emotionally, they deal with high-stress situations, complex cases, and the pressure of life-or-death decisions.
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!
YOUR PATH TO SUCCESS BEGINS HERE
✅ Request information on AUA's MD program TODAY!